Need Help? We are right here!
Search Results:
×






Adaptive MFA or Risk-Based Authentication (RBA) is a smart security feature that adjusts the authentication process based on the risk level of each login attempt. This risk-based approach balances security with user convenience, so only legitimate users gain access while stopping potential threats.
For low-risk scenarios, users enjoy easy access with Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) without any extra steps. When risk is medium or high, the system prompts users to complete additional verification using one of 15+ authentication methods. If the risk is too high, access is blocked to prevent unauthorized entry.
Adaptive MFA builds threat resilience in organizations by blocking modern cyber attacks like phishing, ransomware, etc. It detects insider threats by flagging unusual behavior. Furthermore, it prevents unauthorized access through dynamic responses to risk factors.
Eliminates the need for frequent authentication through a fixed approach. For the calculation of the threats and decisions, the session attributes of the user are fetched during runtime.
Many industries are subject to regulations of local governments and international regulatory bodies, which mandate robust security measures. Adaptive MFA helps organizations meet compliance standards without causing disruptions to daily operations.
Users can be grouped together and given access to specific applications according to their roles based on different access policies.
Admin can track all the user activities, manage access, and add security policies for users on a granular level.
Our Adaptive MFA product is platform-independent and can be easily deployed to any device supporting a web browser, irrespective of the type of device.
Check out Adaptive MFA Demo to see how you can enable risk-based authentication for your applications.
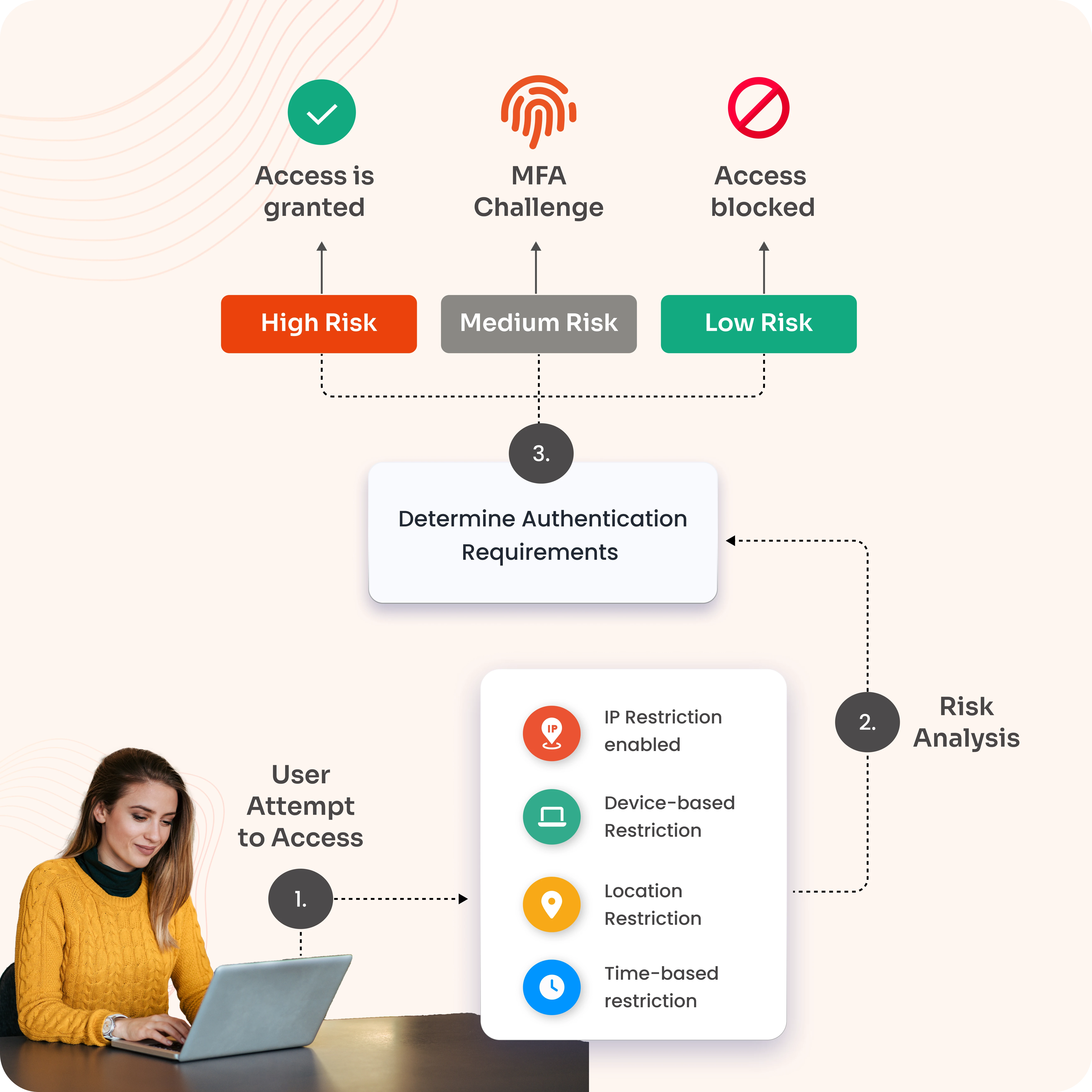
View DemoAdaptive multi-factor authentication adjusts the level of authentication needed based on the risk level of the user's activity. High-risk attempts require additional verification, such as biometrics or OTPs, medium-risk activities trigger moderate checks, and low-risk scenarios grant seamless access. The steps are explained below:
The user attempts to log in or perform an action (e.g., logging in, making a transaction) on a system or application.
The system performs a risk-based authentication assessment by analyzing various factors such as
The process verifies and approves new or unrecognized devices so that only trusted devices can log into a network or system.
The user provides the required authentication factors as requested by the system.
If the user successfully completes the required authentication steps, they are granted access.
*Please contact us to get volume discounts for higher user tiers.
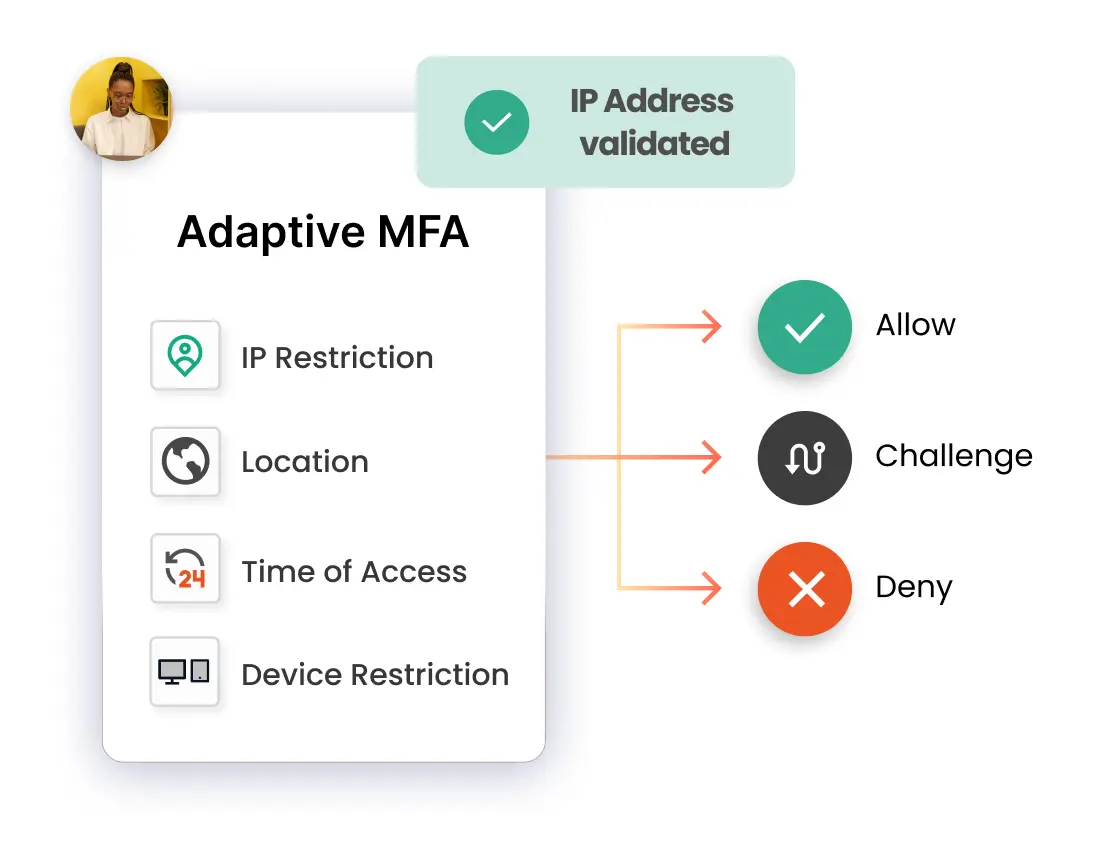
When using IP Restriction as risk-based authentication, IP addresses are configured and enlisted by the admin, and access is either allowed or denied accordingly. When a user attempts to log into one of the risk-based authentication-enabled apps, his IP address is checked against the preset IP list, and appropriate action is taken (i.e., Allow, Deny, or Challenge).
In Location-based Risk-Based Authentication restriction, the admin shortlists and configures a list of Geo-locations. Based on the location restrictions set by the admin, end-users are either allowed or denied the login. When a user tries to log in with Risk-Based Authentication enabled, his location attributes are verified against the location list configured by the admin, and based on this, the user will be either allowed, challenged, or denied access to resources.
Using Device-based Risk-Based Authentication, the admin allows end-users to add a set number of trusted devices (A device refers to a Browser Session). A registered device allows a person to log in without restriction once it has been registered. An administrator will challenge or deny a person's registration if their registered device exceeds their total limit.
Risk-Based Authentication also includes a time restriction, which starts with an admin setting up a time zone with a Start and End Time. Users are permitted, refused, or challenged based on the defined timezone and policies. As soon as an end-user attempts to log in with risk-based authentication enabled, his time zone parameters, such as time zone and system time, are compared to the list defined by the admin, and the user is either granted access, rejected access, or challenged access, depending on his configuration.





I can't speak highly enough regarding miniOrange, I am totally satisfied with the process and results in every regard.
5.0

Awesome tech service, Awesome product. Overall Awesome people. This solution is very simple and easy to implement
5.0
Adaptive MFA strengthens security by dynamically analyzing risk signals (location, device, time, user behavior, etc.) and triggering additional authentication steps only when suspicious activity is detected.
Dynamically adjusts security checks based on contextual aspects such as location, device, or IP address, and authenticates every access request, not just at login, but throughout the user’s session.
Home and public networks often lack enterprise-grade protections, making remote users a prime target for threats. So, dynamic work cultures make it essential to verify every access attempt to protect resources.
Google Workspace Security to protect Gmail, Drive, and other Workspace apps by prompting Adaptive MFA only when risk signals appear. For example, if there is a login attempt from an unknown laptop in another country, the system will allow instant access for trusted users.
Add Adaptive MFA to the VPN network for secure remote access with 15+ authentication methods. For example, if a user attempts VPN access from a new location at odd hours, MFA challenges kick in while regular logins stay friction‑free.
Prevent cyberattacks on apps like Salesforce, Slack, or Dropbox with SSO and MFA solutions. For example, if login behavior deviates from the norm (e.g., sudden access from multiple devices), Adaptive MFA requests extra verification across all connected apps.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) requires users to verify their identity through multiple methods, like passwords, OTPs, or biometrics, for every login. Adaptive MFA, however, adjusts the authentication requirements dynamically based on the assessed risk of each login attempt.
An authentication service is a system or software that verifies the identity of users trying to access a network, application, or resource.
Yes, adaptive MFA blocks threats by detecting unusual behaviors and high-risk indicators associated with phishing and ransomware attacks.
Nested adaptive MFA reduces friction by layering authentication steps based on risk levels.
MFA is a security method that requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to apps or resources.
