Your business functions as a secure base that protects against cyber threats but provides access to authorized personnel. The Identity Provider (IdP) functions as an intelligent security checkpoint that authenticates all user credentials and identifies all users to defend access through secure authentication systems.
The average data breach expense reached 4.88 million dollars during 2024, which established the highest annual increase since previous years, thus requiring businesses to allocate more funds for security protection. The number of corporate network cyberattacks increased by 30% during the past year while security and IT professionals reported they lacked sufficient skills to handle contemporary threats at a rate of 77%.
Identity Providers (IdPs) operate as centralized authentication systems that verify users and control digital identity management to provide secure application access through SSO and MFA functionality. Organizations achieve better security through IdP implementation because it streamlines access management and maintains compliance standards, which enables smooth user experiences between cloud-based and on-premises systems.
Business leaders need to understand IdP functionality because it operates as a core security solution. The article shows how identity management systems boost security operations through enhanced operational efficiency and trust-based systems, both of which lead to organizational success. The article explains various aspects of identity providers in IAM, including how businesses can select their identity provider and why considering miniOrange may be a strong option.
What Identity Providers Really Are
Identity Providers (IdPs) are specialized systems that manage user identities and handle authentication for accessing various applications and services. They serve as trusted authorities that verify user credentials and provide the necessary data to grant access, ensuring secure and efficient identity management.
- Identity Provider: An IdP is a dedicated service that authenticates users by verifying their credentials and supplies critical identity information to connected applications, enabling seamless and secure login processes across multiple platforms. This centralized approach reduces the complexity of managing multiple login systems and improves security oversight.
- User Identity: User identity includes all key attributes and credentials that uniquely define a person in digital systems, such as usernames, passwords, email addresses, roles, group memberships, and additional data like device info or location. Accurate identity representation is crucial for applying appropriate access controls and personalized user experiences.
Importance of IdP in Modern Security
IdPs matter because they centralize identity management to enforce strict security policies, cut password fatigue risks, support compliance standards, and power features like SSO and MFA in today's threat-heavy environments. They also enable organizations to quickly adapt to evolving threats and regulatory requirements, maintaining a strong security posture.
Incorporating identity providers in security strategies strengthens access controls, improves user experience, and protects organizations against evolving cyber threats.
How Identity Providers Work?
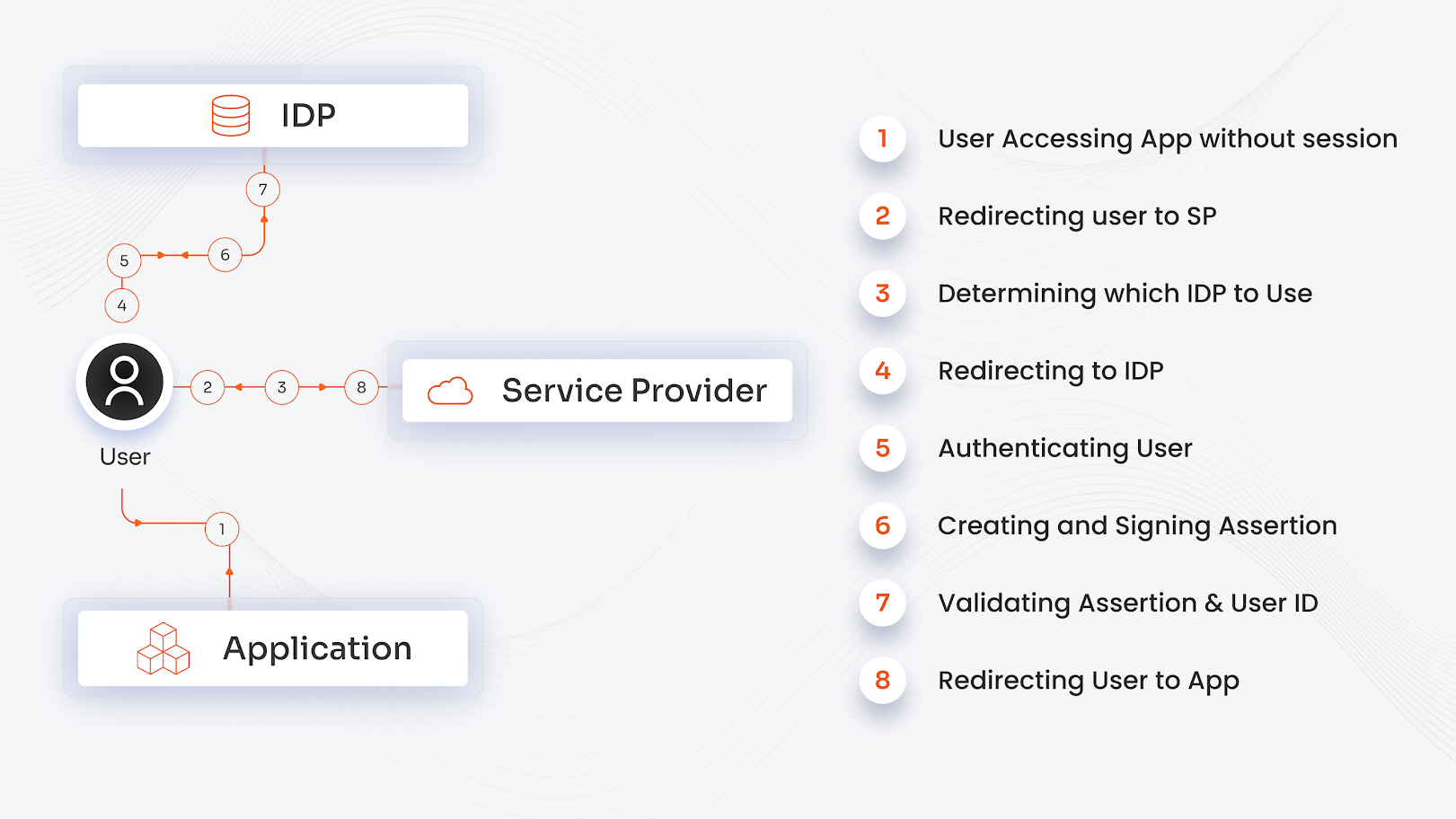
Identity providers (IdPs) are the backbone of modern digital identity management, handling the processes that verify who users are and what they’re allowed to access. They authenticate users by confirming their identity and authorize access by granting permissions based on roles or policies. This workflow ensures secure and seamless user experiences across various applications and services.
- Authentication and Authorization: IdPs validate user credentials during login (authentication) and determine access rights based on predefined rules (authorization).
- Common Protocols and Types of Authentication: IdPs use standards like SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language), OIDC (OpenID Connect), and OAuth to securely exchange identity and access information between users and applications.
- Role in Single Sign-On (SSO): IdPs enable SSO by allowing users to authenticate once and gain access to multiple connected applications without repeatedly entering credentials, improving convenience and security.
Understanding how identity providers operate helps organizations build efficient, secure authentication systems that enhance user productivity and protect sensitive resources.
Security Benefits and Features of Identity Providers
The security posture of an organization depends heavily on identity providers (IdPs) to function properly. The system unifies authentication functions and access management controls, which results in easier user administration and decreased exposure to credential-related security threats. The system provides a strong security structure, which protects against unauthorized access while maintaining regulatory compliance and enabling sophisticated security measures, including multi-factor authentication, to defend your digital assets.
- The system enables users to access a protected authentication system through its secure interface, which defends their login details from security threats.
- The system protects itself from attacks through its ability to limit entry points and enforce security protocols for all applications.
- The system enforces security policies throughout the organization through its uniform access control system.
- The system detects threats in real-time and any suspicious activities, which enables fast responses to potential security breaches and insider threats.
- The system enables organizations to meet security framework requirements through its built-in audit trail system and reporting functionality, which supports SOC 2 and ISO 27001 compliance.
- The system requires users to authenticate their identity through multiple verification steps for multi-factor authentication, which defends against unauthorized system access.
- The system enables users to access multiple applications through a protected single login system, which maintains their user experience.
- The system performs authentication adjustments through risk-based assessments to enhance security at access points.
- The system provides security teams with dashboard access to handle authentication policy management, user activity monitoring and threat response capabilities.
Identity providers enhance security features that protect organizational data and user accounts while making it easier to meet regulatory requirements and manage access permissions.
Types of Identity Providers (IdPs)
Identity providers (IdPs) function as authentication systems that verify users and grant digital identity access to applications and services. The system performs user verification at its core while handling login information and granting protected resource access. Organizations need identity providers to defend their systems while using them for user management and meeting regulatory standards. Organizations protect their passwords from vulnerabilities through IdPs, which enable users to access improved authentication features, including single sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
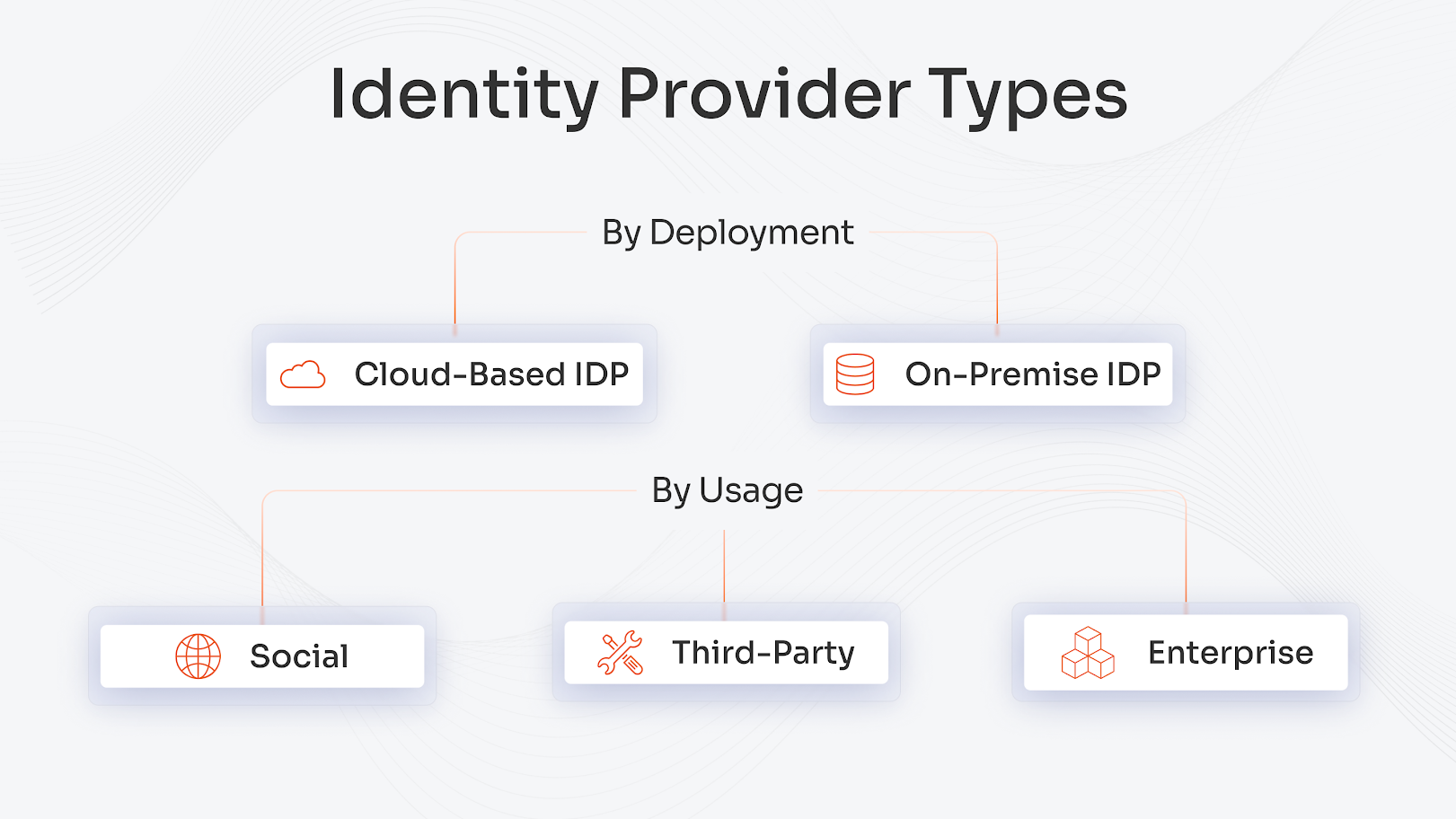
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premises IdPs
Third-party cloud providers operate cloud-based IdPs from their cloud infrastructure. The deployment process of these solutions happens quickly while they receive automatic updates and they scale up or down based on business expansion needs. Okta, Microsoft Azure Active Directory and Google Identity serve as popular examples of cloud-based identity providers. The solutions eliminate infrastructure expenses while enabling global remote access and simplify operations through vendor-managed maintenance services.
Organizations operate their IdPs from their network infrastructure through on-premises deployment. Microsoft Active Directory and LDAP servers function as on-premises identity providers through their role as IdPs. Organizations maintain complete control of their data while they create customized configurations to meet their complex IT system requirements. Organizations that need absolute control over their security policies and data storage choose on-premises IdPs because these solutions meet their strict compliance needs and safeguard sensitive information. On-premises IdPs require an initial setup process, which creates ongoing administrative work for their operation.
The selection between cloud and on-premises identity providers depends on business size and security standards and regulatory requirements and available IT capabilities. Cloud-based identity providers help small to medium businesses achieve faster deployment but large organizations tend to select on-premises systems for their security needs.
| Feature | Cloud-Based IdPs | On-Premises IdPs |
|---|---|---|
| Hosting | Third-party cloud | Internal servers |
| Scalability | Easily scalable | Limited by infrastructure |
| Setup Speed | Rapid deployment | Requires detailed planning |
| Maintenance | Automatic vendor management | Managed by internal IT teams |
| Best suited for | Rapid growth, remote workforce | High-security and compliance needs |
Social, Enterprise, and Third-Party IdPs
Social IdPs enable users to access accounts through their existing social media platforms, including Google and Facebook and LinkedIn. The authentication process becomes easier for user acquisition because users do not need to create passwords when they register. Social IdPs allow users to authenticate through external providers yet organizations surrender their ability to manage identity verification procedures.
Enterprise IdPs serve organizations by handling digital identity management for their employees. The solutions include Okta, Microsoft Azure AD and Ping Identity. The platform delivers advanced security features which include SSO and MFA and policy-based access control for all corporate applications. Enterprise IdPs help organizations achieve efficient user access management while improving productivity through their centralized identity management system and strengthened security features.
Third-party IdPs operate as external identity providers which organizations deploy to obtain additional functionality and connection capabilities. The providers support multiple authentication standards, including SAML and OAuth and OpenID Connect, and allow organizations to create customized identity management processes. The authentication solutions from Auth0 and miniOrange enable businesses to deploy complex authentication systems without requiring homegrown development.
Organizations can select from different IdP types that match their security requirements and user experience needs.
Identity Providers vs. Service Providers
What is a Service Provider (SP)?
A Service Provider (SP) functions as an entity that delivers services together with resources, and applications to end-users. The service provider depends on an identity provider (IdP) to verify user identities before allowing access to its services in identity and access management (IAM) systems.
The online banking application requires your bank credentials, which an identity provider verifies before allowing you to access your account.
Identity Providers vs. Service Providers Compared
| Aspect | Identity Provider (IdP) | Service Provider (SP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Controls identities and verifies users and works as per policies for user permissions | Hosts services or applications to users and enforces authentication |
| Role | Confirms user identity and passes authentication tokens | Verifies authentication tokens and grants access to services |
| Protocols Used | SAML (XML), OIDC (JWT), OAuth (authorization) | Consumes SAML assertions or OIDC ID tokens |
| Examples | miniOrange, Okta, Microsoft Entra ID, Google Workspace | Salesforce, Dropbox, Slack |
| Function in SSO | Centralizes user authentication, enabling single sign-on (SSO) | Relies on IdP for user authentication and grants access based on IdP’s validation |
| Data Managed | Usernames, passwords, attributes, emails, permissions, tokens and assertions | Receives and valides assertions and tokens |
| Interaction Flow | Issues assertions after login, sends to SP | Redirects unauthenticated users to IdP |
| Security Responsibility | Ensures secure handling of user credentials and authentication processes | Ensures secure access to services and resources based on IdP’s authentication |
Practical Use Cases and Integration of Identity Providers
Identity providers (IdPs) create operational value because they enable cross-operational environment functionality. The system enables instant access while strengthening security protocols and decreasing IT operational tasks for all business organizations.
Practical Implementations of Identity Provider Use Cases
- NASA implements miniOrange Crowd SSO to manage authentication for Jira, Confluence, Bitbucket, and Bamboo through a single authentication system that fulfills all necessary compliance requirements.
- The Starbucks organization implements miniOrange SAML SSO for Jira Service Management to provide users with easy login access and separate user accounts and decreased IT support requests.
- The Covance organization uses miniOrange URL-based IdP mapping to provide secure access to Jira SSO through multiple authentication providers.
- Airtel Africa uses miniOrange SSO to defend its Atlassian tools while resolving proxy issues, which creates dependable user access across various countries.
- DPG Media uses miniOrange SCIM provisioning with OneLogin to automate Jira user management, which reduces license expenses and enhances management precision.
Integration with Existing Infrastructure
- The first step for deployment requires identifying all current systems and their connection points through SAML and OAuth and OpenID Connect protocols.
- The organization needs to start with a single department pilot test to identify system problems before expansion while monitoring performance metrics.
- The system performs automatic user and group synchronization between IdPs and Atlassian tools through miniOrange User Sync for immediate updates.
- The implementation of SSO for external users provides operational security protection, which ensures business continuity through normal operations.
- The system uses built-in connectors for HR systems and VPNs and applications to prevent developers from creating custom code.
Scalability and Customization Options
- The system allows user growth management through auto-provisioning and load balancing for handling high traffic volumes.
- The system enables users to create customized workflows that support role-based access and biometric authentication and compliance regulations for their specific environment.
- The miniOrange platform provides adaptable SSO and MFA and SCIM solutions that support businesses of all sizes, from small to large and enable simple growth expansion.
- The system enables users to create their own access request portals, which adjust their functionality based on team size changes.
- The system monitors performance data to achieve operational optimization while keeping the system running without interruption during times of high demand.
Getting Started with Identity Providers
Getting started with an identity provider (IdP) is a smart move for any business that wants to streamline access, boost security, and build trust with users. This section covers the essential steps to evaluate and implement an IdP, tailored recommendations for different business sizes, and how miniOrange’s solutions can help you succeed.
Steps to Evaluate and Implement an IdP
- Start by assessing your business needs: Do you require single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), or social login capabilities?
- Evaluate scalability and flexibility: Choose an IdP that can grow with your organization and adapt to changing requirements.
- Check integration options: Make sure the IdP supports your existing applications and platforms, such as Active Directory, cloud services, or custom apps.
- Review user management features: Look for tools that let you assign roles, manage permissions, and automate user provisioning.
- Prioritize support and reliability: Select a provider with a strong support team and proven uptime to minimize disruptions.
- Verify compliance: Ensure the IdP meets relevant security and privacy standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific regulations.
Recommendations by Business Size
| Business Size | Recommended IdP Features | Example Providers |
|---|---|---|
| Small Business | Simple setup, affordable pricing, easy user management | miniOrange, OneLogin |
| Mid-Sized Business | Scalable, multi-app integration, MFA support | miniOrange, Ping Identity |
| Enterprise | Advanced security, analytics, custom workflows, wide integrations | Okta, Microsoft Azure AD and miniOrange |
Small businesses benefit from solutions like miniOrange, which offer quick deployment and responsive support for SMBs. Mid-sized businesses need scalable solutions that can handle increasing user loads and complex integrations. Enterprises require advanced features like analytics, workflow automation, and compliance tools.
How Does the miniOrange Identity Provider Help You?
miniOrange provides flexible identity management for businesses of all sizes. Their solutions include:
- Seamless SSO for cloud and on-premise apps
- Easy-to-deploy MFA and passwordless authentication
- Unified administration for centralized user management
- Responsive support and detailed documentation
This approach ensures your readers get clear, actionable advice and see miniOrange as a trusted partner for identity management. Find the right fit for your business and start building a secure, user-friendly access experience. Experience superior identity management with miniOrange. Try today.
FAQs
What does IdP stand for?
IdP stands for Identity Provider. An Identity Provider is a system or service that verifies user identities and handles authentication so users can securely access applications, websites, or networks.
What is an IdP?
An IdP functions as a system that creates digital identities of users and helps them access protected applications and services through authentication.
What is an example of an IdP provider?
Users can enter their existing credentials to access applications through IdP providers, such as miniOrange, Google, Microsoft, and Okta.
How does an IdP improve security?
The IdP system provides security benefits through its central user authentication system and multi-factor authentication and complete access log storage for compliance requirements.
What protocols do IdPs use?
IdPs rely heavily on protocols such as SAML, OAuth, and OpenID Connect to authenticate user identities as per the application in which the user wants to log in. It also enables SSO functionality while granting them different privileges according to defined policies.
How to choose the right IdP for my business?
Select an IdP solution that matches your organization size and meets security standards and supports required protocols and offers simple integration and fulfills all necessary compliance standards.
What is the difference between IdP and SP?
The IdP system verifies user identity and authenticates them to enter into an application, but service providers (SPs) will work after the successful authentication to authorize service access, which is dependent on IdP.




Leave a Comment